 |
Hyemoschus aquaticus
Cervatillo de agua (Sp), Hirschferkel (G), Chevrotain aquatique (F).
DESCRIPTION Shoulder height 12-16 inches (30-40 cm). Weight 15-33 pounds (7-15 kg); males average 21 pounds (9.7 kg), females average 26 pounds (12 kg).
The water chevrotain is a compact animal with a thick neck, humped back, heavy hindquarters and long, slim legs. The head is small, with a pointed snout and small ears. The coat is a rich brown with longitudinal white stripes and rows of bold white spots. There are white stripes on neck and jaw, and the short tail is white underneath. Although normal facial and foot glands are absent, there are scent glands on the chin that are unique to chevrotains. Instead of horns or antlers, the upper canines are developed into tusks, similar to those of water deer and musk deer, but smaller. Females are larger than males, but have shorter, blunter tusks.
BEHAVIOR Essentially solitary, living on widely spaced home ranges with minimal contact. Females are usually solitary, or with suckling young, on home ranges that average 32-35 acres (13-14 hactares). Males live alone on 50-75-acre (20-30 hactares) home ranges that overlap the ranges of at least two females. Males are often wounded in fights over space, attacking openmouthed and swiping with their sharp tusks. Females also fight, but are less aggressive. When fighting they emit a high-pitched chatter, scream when wounded and bark when alarmed. The throat and rump in both sexes are protected from tusk wounds by thick skin and deep muscles. Females are thought to bear one young annually, after a gestation period that is variously reported as four months or 6-9 months. Young are nursed 3-6 months and disperse at nine months, when they are sexually mature. Fully grown at two years. Life expectancy about eight years, though may be as long as 11-13 years.
Nocturnal, resting by day in a hidden place. Usually near water, but enters water only when there is danger. Defense from predators is concealment or "freezing" motionless, with underwater swimming a last resort. Feeds almost exclusively on fallen fruit.
HABITAT Lowland equatorial rain forest, in river valleys and the edges of streams and swamps.
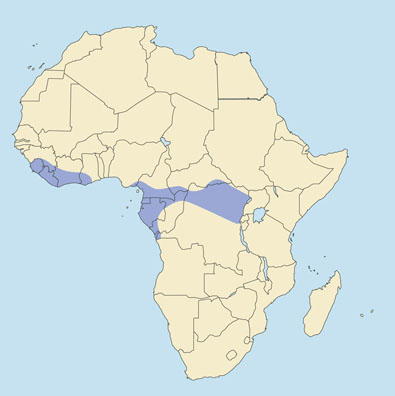
DISTRIBUTION West Africa: Sierra Leone to Ghana. Central Africa: southeastern Nigeria, southern Cameroon, Gabon, Congo (B), southern C.A.R., and northern Congo (K). Possibly still occurs in western Uganda.
REMARKS Best hunted after dark with a headlamp, where legal. Its flesh is delicious.
TAXONOMIC NOTES Three subspecies have been described, but are not considered valid.
STATUS Numbers are estimated at several hundred thousand, but are declining in many areas from habitat loss and overhunting by locals for meat. Listed on CITES Appendix III.
|





