 |
 |
Capra nubiana
Ibice de Nubia (Sp), Nubischer Steinbock (G), Bouquetin de Nubie (F). Named after the Nubian region in northern Africa, which includes parts of Egypt and Sudan. Also called beden (Arabic), or mideastern ibex.
DESCRIPTION Shoulder height 25-33 inches (64-84 cm). Weight 100-150 pounds (45-68 kg).
The Nubian ibex is smaller and more lightly built than the other species of true ibex (please see Asia for text on true ibex). The general color is yellowish-brown, with a dark dorsal stripe and dark markings on the chest. Underparts and chin are whitish. Legs have conspicuous black and white markings from the knees and hocks downward. The beard, while narrow, is long and dark. The short tail has a tuft of stiff black hairs. Ears are large, measuring 4-5 inches (10-12 cm) in length. There are scent glands under the tail. The male's horns are long, rather narrow, and scimitar-shaped, forming three-fourths of a circle. The front surface is flattened at an obtuse angle, so that the outer edge is rounded and the inner edge is sharp, and it is strongly cross-ridged. Females are smaller than males, lighter in color, beardless (except that very old females may have small beards), and grow horns only 5-6 inches (12-15 cm) in length.
The Nubian ibex is distinguished from the Asian and Alpine ibexes by its narrower horns with their rounded outer edges, its white belly, and its contrasting black and white leg markings. It shares the characteristic of black and white leg markings with the walia ibex, but lacks the bony boss on the forehead.
BEHAVIOR Lives in small mixed herds, though males are often solitary. Breeds mainly during October-November, usually with one kid (though often two) born 5-1/2 months later. Females go apart from the herd to give birth, taking refuge in caves or beneath overhangs. Longevity in captivity can exceed 10 years.
Feeds early morning and late afternoon, but also at night when hunted hard. Eats grasses, bushes and foliage. Will stand on its hind legs to browse from bushes or trees. Has to survive with little or no water during much of the year. Eyesight, hearing and sense of smell are exceptional. An extremely agile climber on the steepest rock.
HABITAT Arid desert hills and mountains from sea level to 6,000 feet (1,800 m).
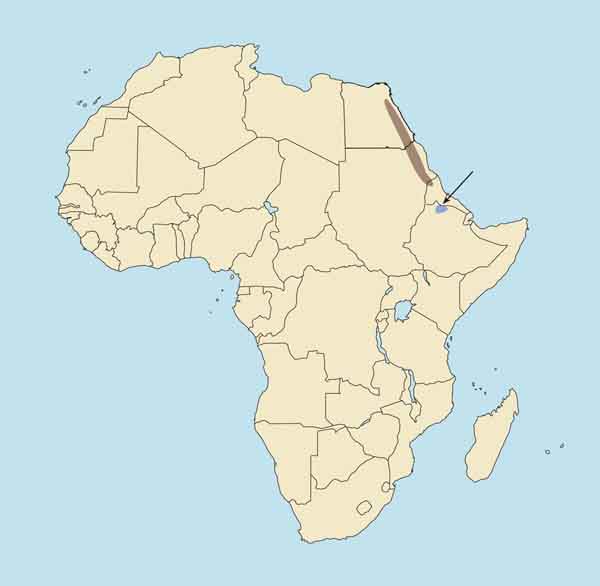
DISTRIBUTION The Red Sea Hills in Egypt and Sudan, and the mountains of Eritrea.
Outside Africa, Nubian ibex are found in the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt, and in Israel, southwestern Jordan and the Arabian Peninsula. Formerly in Lebanon and Syria, but no longer to be found there. Introduced in the Tatra Mountains of eastern Europe, where it is said to have interbred with reintroduced Alpine ibex and introduced bezoar ibex; if true, this would be an unfortunate biological mistake. Nubian ibex have also been introduced on game ranches in several parts of the world.
REMARKS An excellent game animal, as are all wild goats. It lives in some of the most harsh, least hospitable terrain on Earth, where it has been persecuted for centuries by local people. Hunted by glassing and stalking, by conducting drives, or by waiting at waterholes. The first two require fitness on the part of the hunter; all require long-range shooting ability, often at a moving target. Success is by no means certain.
TAXONOMIC NOTES Includes these named forms: arabica (Sinai), beden (southwestern Arabia), mengesi (southeastern Arabia), nubiana (upper Egypt), sinaitica (Sinai), and typica. We do not separate them, as scientists are unable to find any consistant differences.
|





