 |
Hyaena hyaena dubbah
DESCRIPTION Length, including tail, 4-5 feet (120-150 cm), sometimes more. Shoulder height 24-30 inches (61-76 cm). Weight 55-100 pounds (25-45 kg), sometimes more. Males and females are about the same size.
The smallest hyena, with long, pointed ears and a long, bushy tail. Its coat is long, coarse and shaggy. It varies in color from gray to yellowish-gray, and has a number of black stripes on body and legs. The muzzle, throat and neck are mostly black, and there are two black cheek stripes. An erectile mane of long, black-tipped hairs extends from neck to rump. The external genitalia are normal, unlike those of the spotted hyena.
BEHAVIOR Usually solitary or in pairs, rarely in small packs (at a carcass, for example). Females are intolerant of each other and are dominant over males. May defend a small territory around the breeding den. Breeding takes place throughout the year, with usually 2-4 young (range is 1-5) born after three months gestation. Sexually mature at 2-3 years. Longevity as much as 23-24 years in captivity.
The striped hyena is mainly nocturnal or crepuscular, remaining hidden during the day. It is wary of the larger spotted hyena and avoids it. Mainly a scavenger of carrion, it also kills small animals, birds, snakes and even insects, and eats fruit and agricultural crops. In North Africa (where it attains a larger size than elsewhere) it preys on domestic goats, sheep, donkeys and horses. When surplus food is available it will hide some for future use. Drinks daily when water is available. Much more shy and elusive than the spotted hyena, and less noisy and aggressive. Senses of smell and hearing are very good, eyesight is good. A slower runner than the spotted hyena.
The striped hyena has been known to attack and kill people, especially children. However, it can be tamed, and is said to make a loyal and affectionate pet. In some areas, many of its body parts are valued for folk medicine.
HABITAT Open or rocky country at elevations up to about 11,000 feet (3,350 m). Avoids true deserts, and is said to require water within about six miles (10 km). Some thick cover is essential.
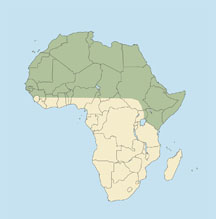
DISTRIBUTION Across northern Africa from Morocco and Senegal to Egypt, then southward in Sudan, Ethiopia, Somalia, Uganda and Kenya to mid-Tanzania.
It also occurs across southern Asia, from Asia Minor and the Arabian Peninsula eastward to India. The striped hyena is the only hyena found outside Africa. It is generally rare within its range.
TAXONOMIC NOTES Three subspecies are listed in Africa: barbara (Morocco to western Libya), dubbah (south of the Sahara), and vulgaris (eastern Libya and Egypt). They are combined here, with dubbah Meyer, 1791 having priority.
STATUS The subspecies barbara is listed as endangered by the IUCN and the USF&WS. It has declined from habitat loss and because it has been persecuted as a predator.
|





